Lenses
Lens is an object, usually made of glass, bounded by one or two spherical surfaces.
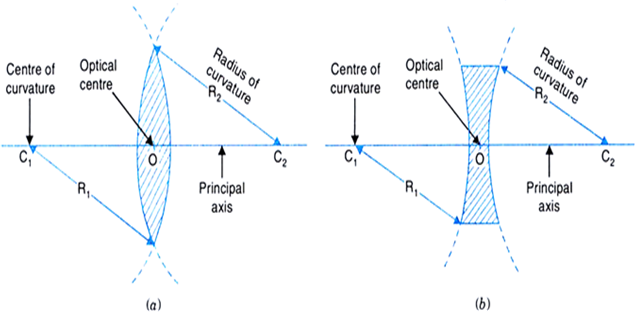
Types of lens: (i) convex or converging lens (ii) concave or diverging lens
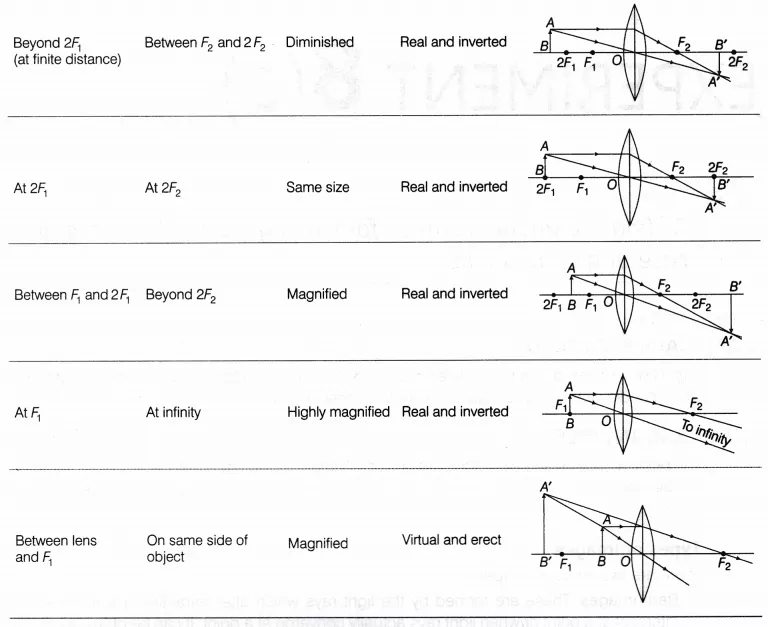
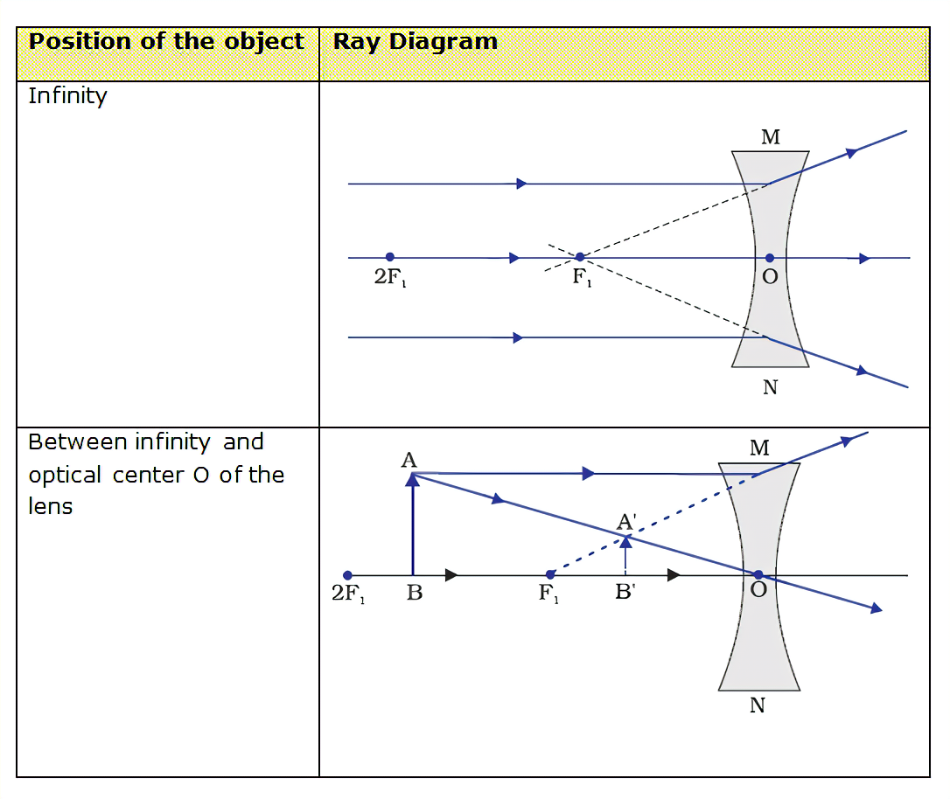
Lens formula : The relation between object distance u, image distance v, and focal length f of a lens is known as lens formula .
=+
Len's maker's formula : The relation between focal length of a lens, radii of curvature of two surfaces and refractive index of the material is called lens maker's formula.
=(-1)(+)
Combination of thin lens
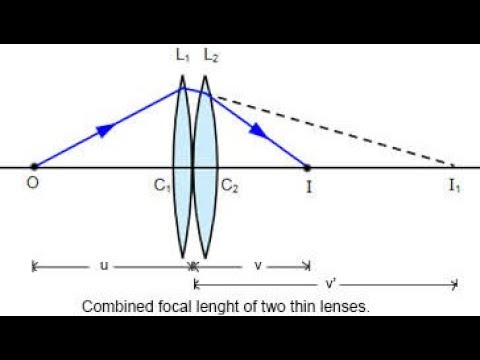
=+
Power of a lens is a measure of its ability to produce deviation of light.
Power of a lens, P=
Magnification of a lens is defined as the ratio of the size of image produced by it to the size of the object.
- m=====
Optical centre is the geometrical centre of the lens through which light never bends after passing through.
Displacement formula,
- Focal length of a lens depends on radius of curvature, refractive index of the lens and that of the surrounding medium.
- An air bubble inside the water behave as diverging lens.
- If one of the surface of a lens is painted to make a mirror, then it behave as a combination of two lens and one mirror.
- Intensity of the images proportional to the square of the aperture of the lens.
- Minimum distance between the real object and real image by a convex lens is four times the focal length.
- If the object is kept between optical centre and the focus of a biconvex lens, then it behaves as a magnifying lens.
- The plane perpendicular to the principle axis at the focal point is called focal plane.
- A sun glasses has no power.
- Depending on the refractive index of the surrounding medium, the nature of the lens can be changed.
- If a portion of a lens is broken still, then it will form the complete images.