Navigation
Mechanics
Heat and Thermodynamics
Heat and TemperatureTemperature ScaleMeasurement of heat energy and Specific heat energyLatent HeatSaturated and Unsaturated VapourRelative humidity and dew pointThermodynamics.Reversible isothermal and adiabatic changesFirst Law Of ThermodynamicsHeat Transfer ConductionConvection RadiationSolar Constant and Important NotesGas lawsKinetic theory of gasesSecond Law of thermodynamicsCarnot's engineExpansion of SolidExpansion of Liquid and Gas
Magnetism
Geometrical Optics
Wave Optics
Electrostatics
Current Electricity
Saturated and Unsaturated Vapour
Saturated Vapour
Vapour that can't hold more liquid molecules at given condition and does not follow gas law.
UNSaturated Vapour
Vapour that can hold more liquid molecules at given condition and follow gas law.
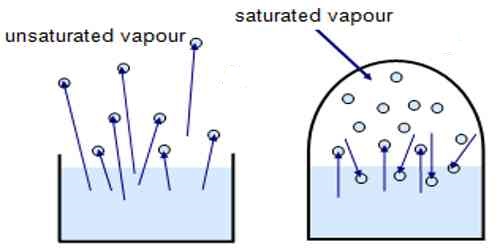
Effect of volume on saturated vapor.
- The saturated vapor at given volume, on increasing volume it becomes unsaturated.
- The saturated vapor at given volume, on decreasing volume, vapor remain saturated giving out more liquid molecules.
Effect of temperature on Saturated Vapor.
- When the temperature of saturated vapor increase then it becomes unsaturated.
- When the temperature of saturated vapor decrease then it remains saturated giving out more liquid.
Effect of pressure
On Melting Point:
- Melting point of a body decrease on increasing temperature pressure if volume decrease on melting. E.g. ice
- Melting point of body increase on increasing pressure if volume increase on melting. E.g. Wax
On boiling point:
- Liquid boil if the total pressure on it's surface become equal to the saturated vapor pressure so the boiling point increase on increasing pressure.
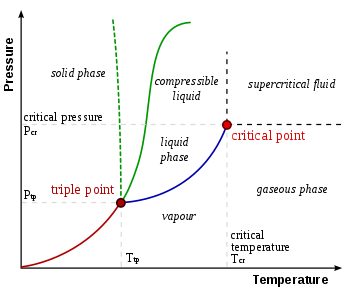
Triple Point
Points on P-T diagram at which 3 states of matter i.e. solid, liquid and gaseous state coexist, fusion curve, sublimation curve and vaporization curve meet. It is standard point in thermometry since it is unique. It's value is 4.58mm of Hg pressure and 273.15K temperature for water and 5.11 atm pressure and -56.6C temperature for carbondioxide.
Evaporation:
- Process of escaping liquid molecules from its surface by taking energy from surrounding molecules.
- Cooling is observed after evaporation and takes place at all temperature and which stop if vapor is saturated.