Navigation
Mechanics
Heat and Thermodynamics
Heat and TemperatureTemperature ScaleMeasurement of heat energy and Specific heat energyLatent HeatSaturated and Unsaturated VapourRelative humidity and dew pointThermodynamics.Reversible isothermal and adiabatic changesFirst Law Of ThermodynamicsHeat Transfer ConductionConvection RadiationSolar Constant and Important NotesGas lawsKinetic theory of gasesSecond Law of thermodynamicsCarnot's engineExpansion of SolidExpansion of Liquid and Gas
Magnetism
Geometrical Optics
Wave Optics
Electrostatics
Current Electricity
Thermodynamics.
Thermodynamics:
- Branch of physics which deals with the study of relationships involving heat, mechanical work, and other aspects of energy and energy transfer.
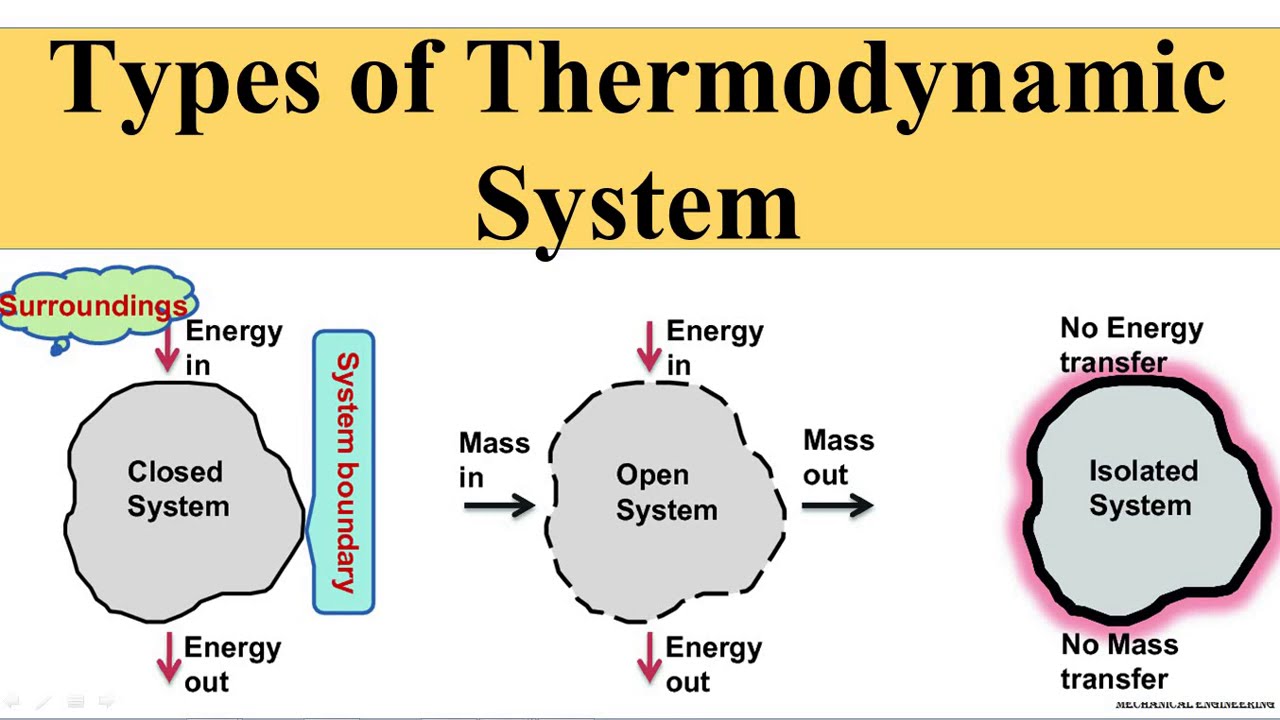
Thermodynamics system:
- It is an assembly of an extremely large number of particles (atoms or molecules) having a certain pressure, volume and temperature.
- It is of two types:
1) Isolated System: (no heat can enter or leave out the system)
2) Closed system: (There can be heat exchange between the system and surrounding)
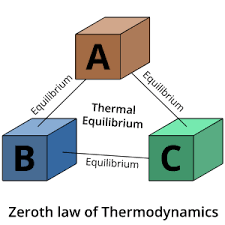
Thermal Equilibrium:
- A thermodynamics system is in thermal equilibrium if the temperature of all parts of it is same.
Zeroth law of Thermodynamics:
- When two bodies A and B are in thermal equilibrium with third body C then the body A and B also must be in thermal equilibrium with each other.
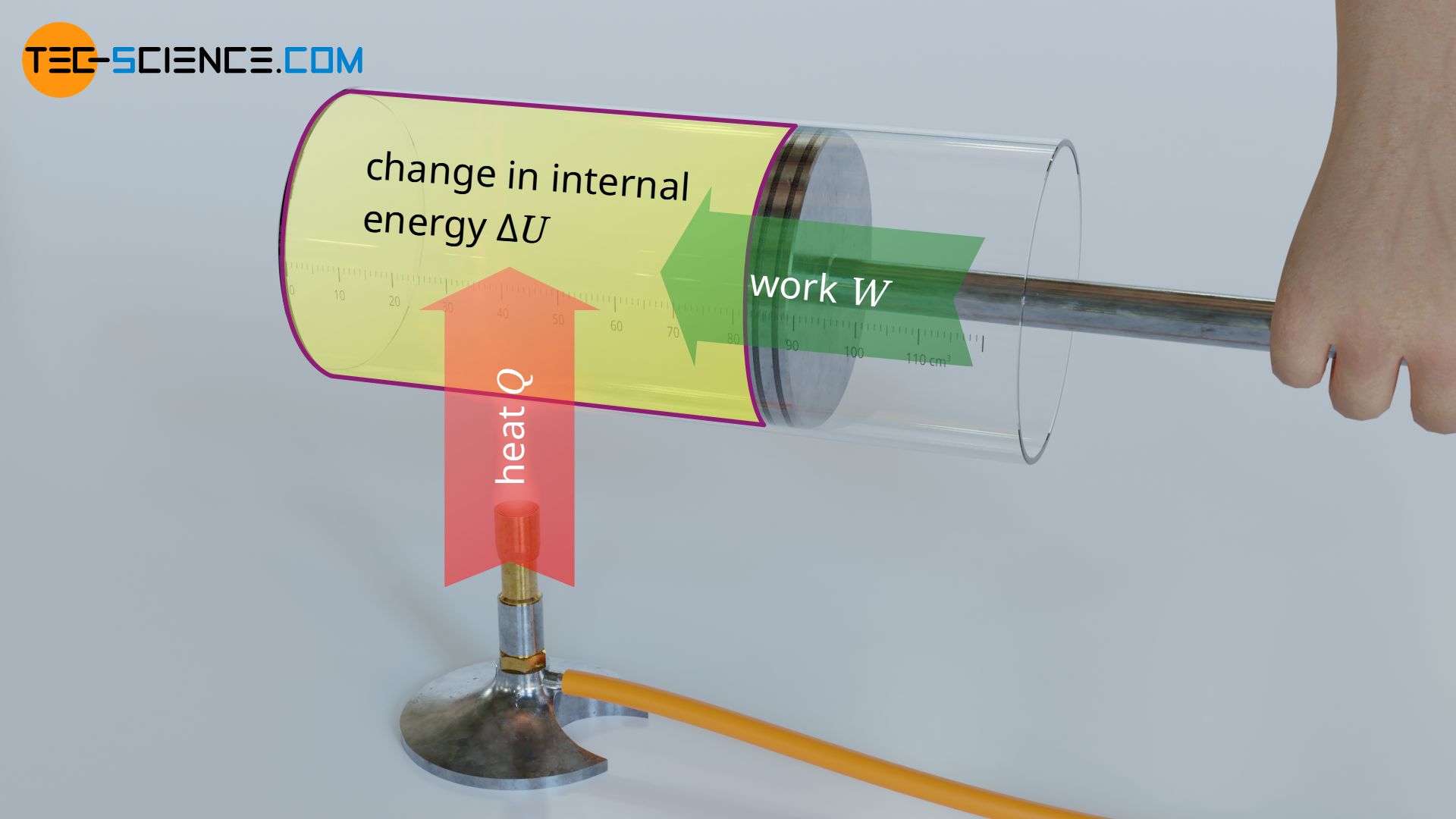
Work Done:
- Work is said done when volume of gas changes.
- Work done is positive if expansion takes place and is negative if compression takes place.
- Work (W) = PdV
- Area under PV curve between volume axis is equal to work done.
- For a closed cycle, area of closed loop gives work done.
- When P remains constant throughout the expansion, the work done by the gas is
Internal Energy of a Gas
- The sum of energy due to molecular motion (KE) and due to molecular configuration (PE) is called internal energy of gas
Note:
For ideal gas intermolecular force of attraction is neglected i.e. PE=0, so internal energy of ideal gas is KE which is only the function of temperature.