Navigation
Mechanics
Heat and Thermodynamics
Heat and TemperatureTemperature ScaleMeasurement of heat energy and Specific heat energyLatent HeatSaturated and Unsaturated VapourRelative humidity and dew pointThermodynamics.Reversible isothermal and adiabatic changesFirst Law Of ThermodynamicsHeat Transfer ConductionConvection RadiationSolar Constant and Important NotesGas lawsKinetic theory of gasesSecond Law of thermodynamicsCarnot's engineExpansion of SolidExpansion of Liquid and Gas
Magnetism
Geometrical Optics
Wave Optics
Electrostatics
Current Electricity
Conduction
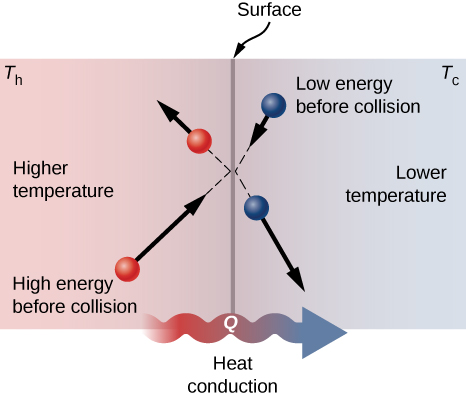
Conduction:
- No actual movement of molecules takes place.
- Takes place mainly in solid and partially in liquid and gas.(reason > distance between molecules)
- Metals are good conductor of due to presence of free electrons in it.
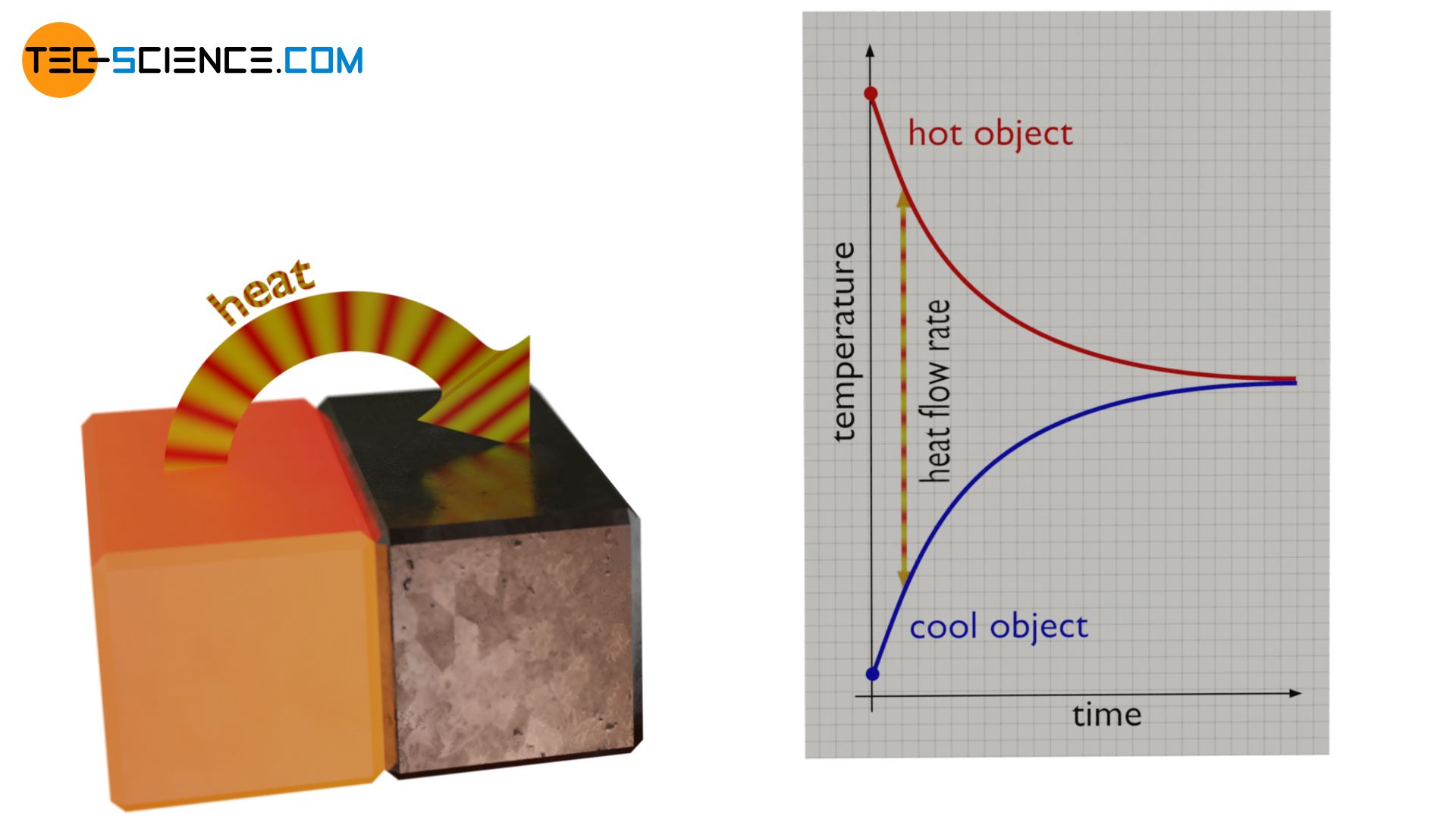
- Steady state => No heat loss by leakage and rate of flow of heat is same throughout the conductor.
- Non-Steady state = Rate of heat flow varies from point to point. In this case heat loss takes place from body of conductor.
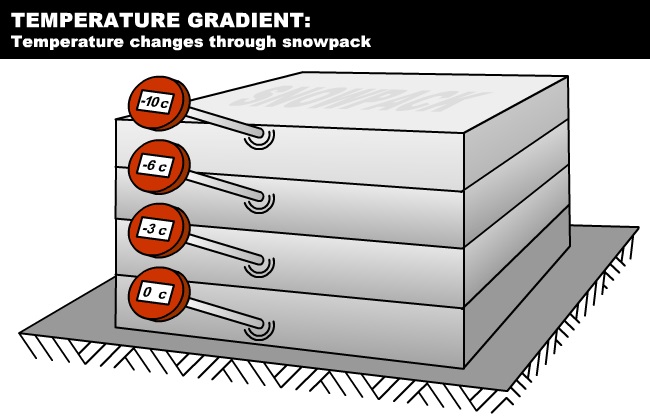
Temperature gradient:
- The rate of fall of temperature with distance in the direction of heat flow is called the temperature gradient.
- Temperature gradient= (Where L is the distance between the point with temperature 1 and 2)
Rate of flow of Heat
- The rate of flow of heat across a cube of side ‘l’ having face of area ‘A’ at different temperature 1 and 2 area depends on
- Area of face of cube
- Temperature difference of opposite faces
- Distances of faces
Where, K is the thermal conductivity of matter of unit whose value depends on nature of conductor
NOTE:
Silver has the highest thermal conductivity.
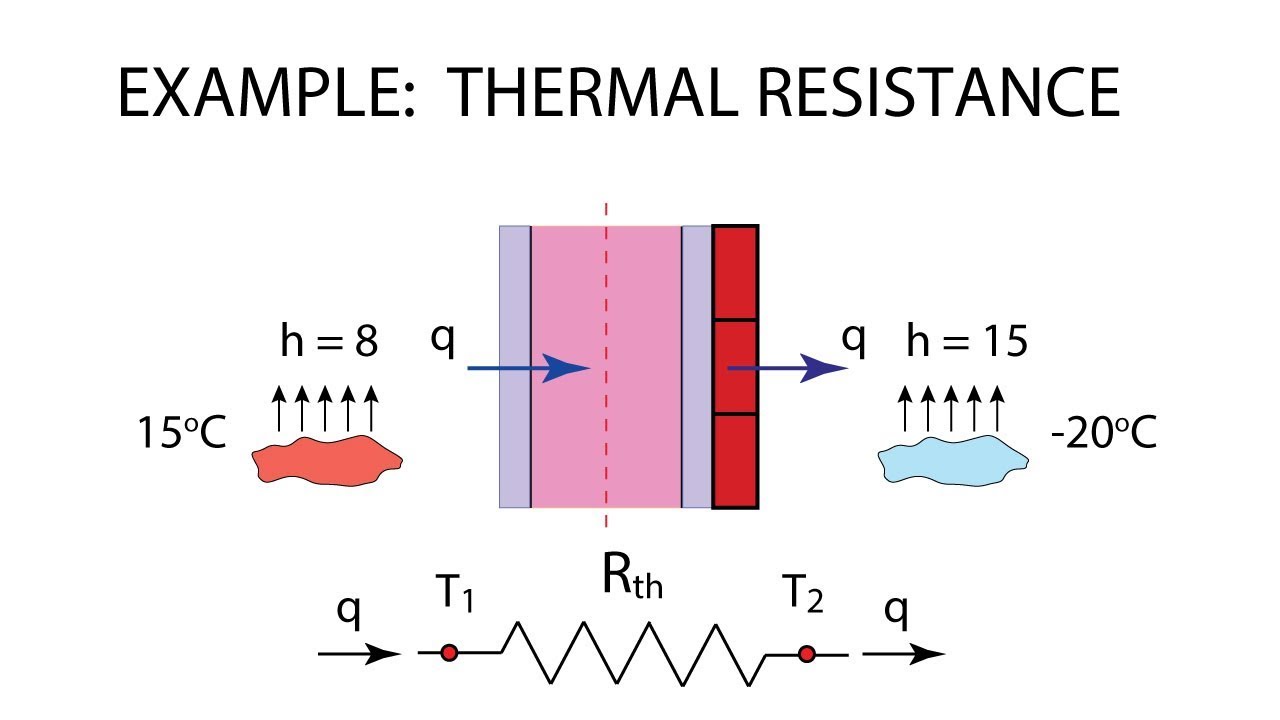
thermal resistance
Where = Rate of flow of heat is called heat current
=Temperature difference is equivalent to potential difference
=R is called the thermal resistance which oppose the flow of heat current
Combination of conductor
Series Combination => = => =
Parallel Combination =>=
=>
Thermal conductivity of a good conductor by searle's method:
K=
Where, K is the thermal conductivity of the rod
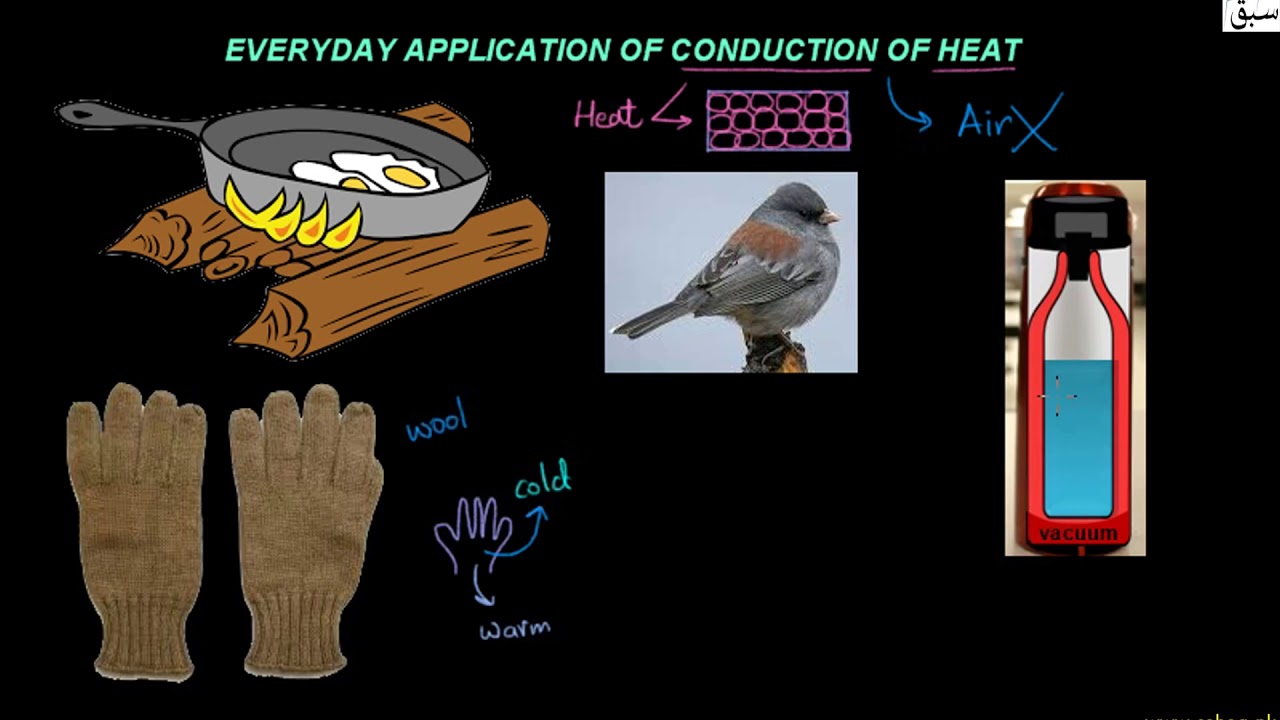
Application of Conduction:
- Ice is packed in saw dust(reason: wood and air are bad conductor or heat)
- Woolen clothes are warm because they have fine pores filled with air. (wool and air are bad conductor of heat)
- Eskimos make double walled houses of the blocks of ice. ( air enclosed between the double wall is …..(good/bad) conductor of heat. Ans = bad)